Biophysics of the Endocannabinoid System
The human body is an incredible communication network. Every second, billions of cells exchange signals using electromagnetic vibrations and frequency-based responses. Enzymes activate these reactions, and endocannabinoid receptors receive messages that help regulate key functions.
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) acts as a bridge between body, mind, immune response, and emotions. It becomes especially active when we are in natural environments or experience positive social contact. That’s when the body produces endocannabinoids – internal messengers that help restore balance.
Certain plants, like hemp, contain similar molecules called phytocannabinoids. When consumed as part of the complete plant matrix (the so-called "phyto-complex"), they can naturally align with our Endocannabinoid System (ECS) – an essential balance in today's hectic, stress filled world.
ECS & Reproduction: Nature’s Guardian System
Did you know the ECS is also involved in reproduction? According to researcher Dr. Mauro Maccarrone, it’s the “guardian angel” of fertility. This system influences the entire reproductive process – from sperm production to fertilization, embryo implantation, and fetal development. ECS receptors are especially abundant in the placenta, helping the embryo and mother communicate effectively.
Biochemistry: How the ECS Works
The endocannabinoid system consists of three main components:
- Endocannabinoids like anandamide and 2-AG, produced on demand
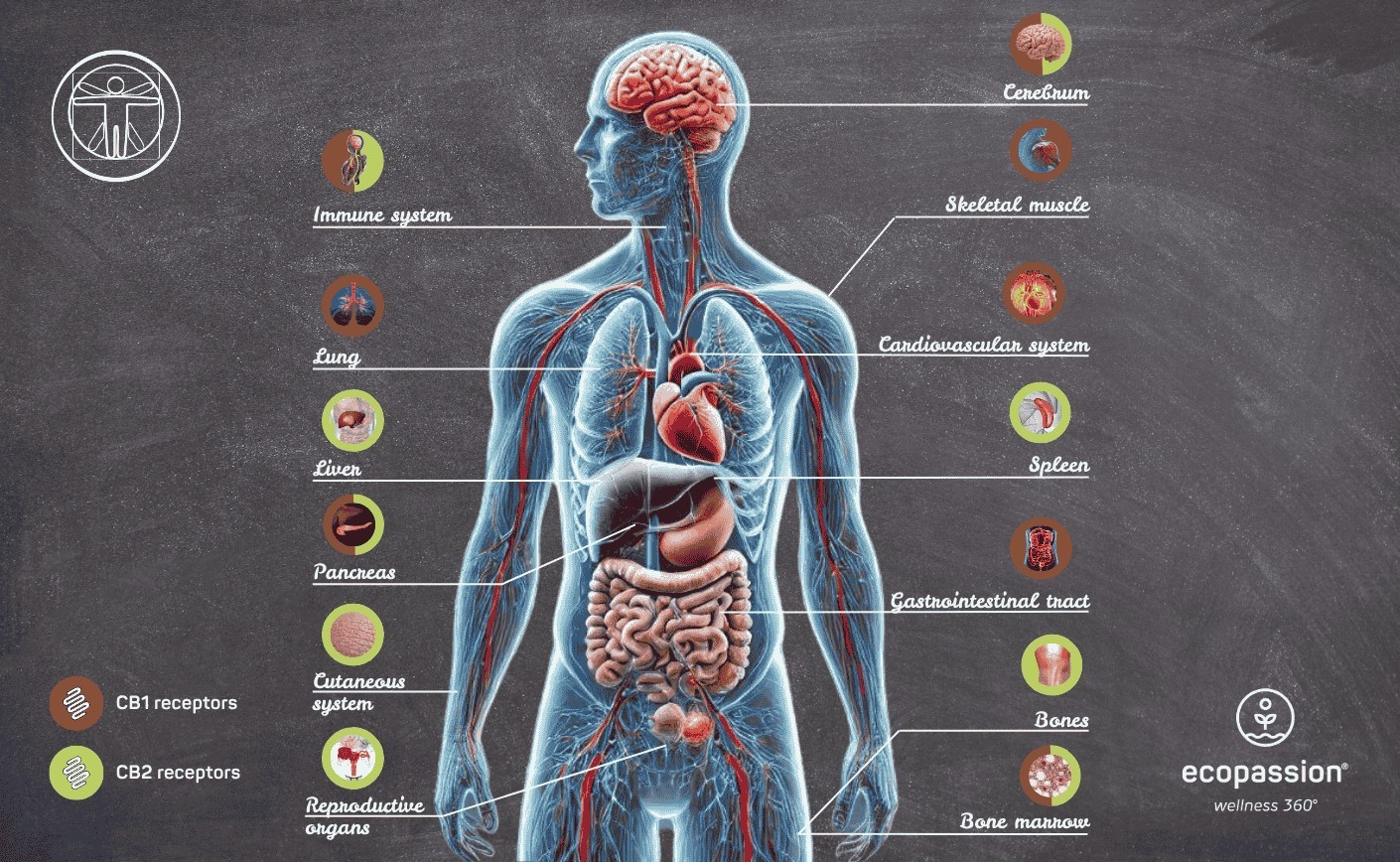
- Receptors (CB1 and CB2), which transmit signals to the cells
- Enzymes, which break down these molecules after use
Together, these components help the body adapt to stress, pain, and internal changes. The ECS works closely with the immune system, yet operates independently.
Key Receptors: CB1, CB2, and GPR55
CB1 – The Nervous System Receptor
These receptors are primarily located in the brain and spinal cord, but are also present in the uterus and the digestive tract. CB1 helps regulate the central nervous system and protects against sensory overload.
CB2 – The Immune Receptor
CB2 receptors are primarily located in immune cells. They are responsible for regulating inflammatory responses and supporting immune defense. CB2 is also present in the nervous system — especially in so-called microglial cells, which protect and repair damaged nerve cells.
Studies suggest that CBD may interact with CB2 receptors to reduce pro-inflammatory messengers such as cytokines. This mechanism could, for example, help in cases of neuropathic pain.
GPR55 – The “CB3”?
This receptor is still under investigation. It may play a role in conditions like epilepsy and is sometimes labeled the third cannabinoid receptor. However, research is still in its early stages. What is clear, though, is that this receptor is also part of the fascinating puzzle of the Endocannabinoid System.
Conclusion
The ECS is a subtle but essential system that influences:
- Pain perception
- Inflammation
- Stress regulation
- Hormonal balance
- Immunity
- Reproductive health
With the gentle support of plant-based cannabinoids, the ECS can help the body maintain balance–naturally and intelligently.
Author: Prof. Alberto Frattini
Naturopathy expert, kinesiologist